Local parameters
SENSR's perception is powered by a pipeline of algorithms. To achieve the best results for your specific environment, you can fine-tune these algorithms using parameters.
By default, these parameters are applied to an Algo Node, which typically covers a specific geographical area. For more details on this concept, please review our System Architecture documentation.
A common challenge is needing different parameter sets for different zones within a single LiDAR's field of view—for example, an open road versus a cluttered intersection. The Sensor Mirroring feature solves this. It allows you to create a virtual copy of a LiDAR's data stream and process it in a separate Algo Node with its own unique geographic boundary and tuning parameters.
This lets you apply highly customized settings to different areas without needing to install additional physical sensors.
When to Use Sensor Mirroring: This powerful feature is intended for zones that require significantly different parameter settings. For minor adjustments across a site, it's often better to only tune the primary Algo Node.
Step-by-Step Guide
Follow these instructions to configure local parameters for a specific area on your site.
- Create a new, dedicated Algo Node.
- Add a
Mirror LiDARto this new node, selecting the source LiDAR to mirror. - Define the precise geographic coverage for the new Algo Node.
- Set the custom parameters for that node.
Step 1: Create a New Algo Node
First, you need a new container for your local parameters.
- While in Project Mode, click the
+ New Algo Nodebutton. - A pop-up window will appear. Configure the new node:
* **Name:** Give it a descriptive name (e.g., "Parking_Lot_Zone").
* **Use GPU:** Tick this box if you need to detect vehicles or other classes that rely on deep learning.
* **Preset:** Select a suitable base configuration (e.g., `outdoor_gpu`, `indoor`).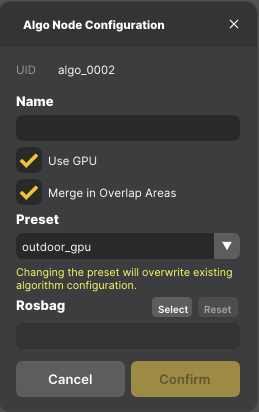
Step 2: Add a Mirror LiDAR
Next, populate the new Algo Node with the virtual sensor.
- With the new Algo Node created, click the
+ Add Sensorbutton inside its panel.
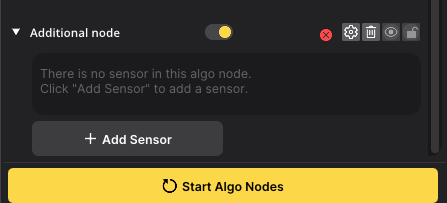
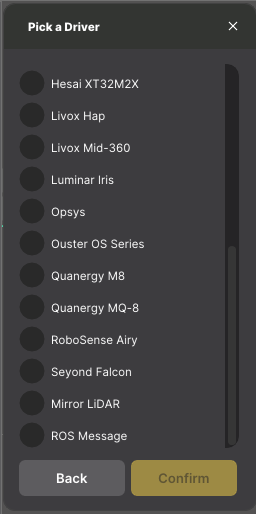
- In the pop-up that appears, scroll down and select the
Mirror LiDARoption.
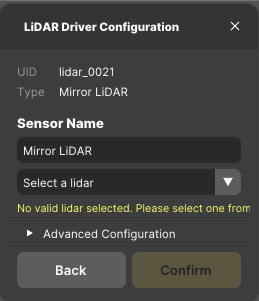
- In the LiDAR Driver Configuration window, use the dropdown menu to select the topic of the physical LiDAR you wish to mirror.
- Click
Confirm.
Step 3: Define the Algo Node Coverage
Now, you must define the exact geographical area where your new parameters will apply.
- Click on the new Algo Node's title bar to select it.
- Press the
Ykey on your keyboard to enter coverage editing mode. - Resizing handles will appear on the corners and edges of the Algo Node's boundary box. Click and drag these handles to resize the area precisely over the desired zone.
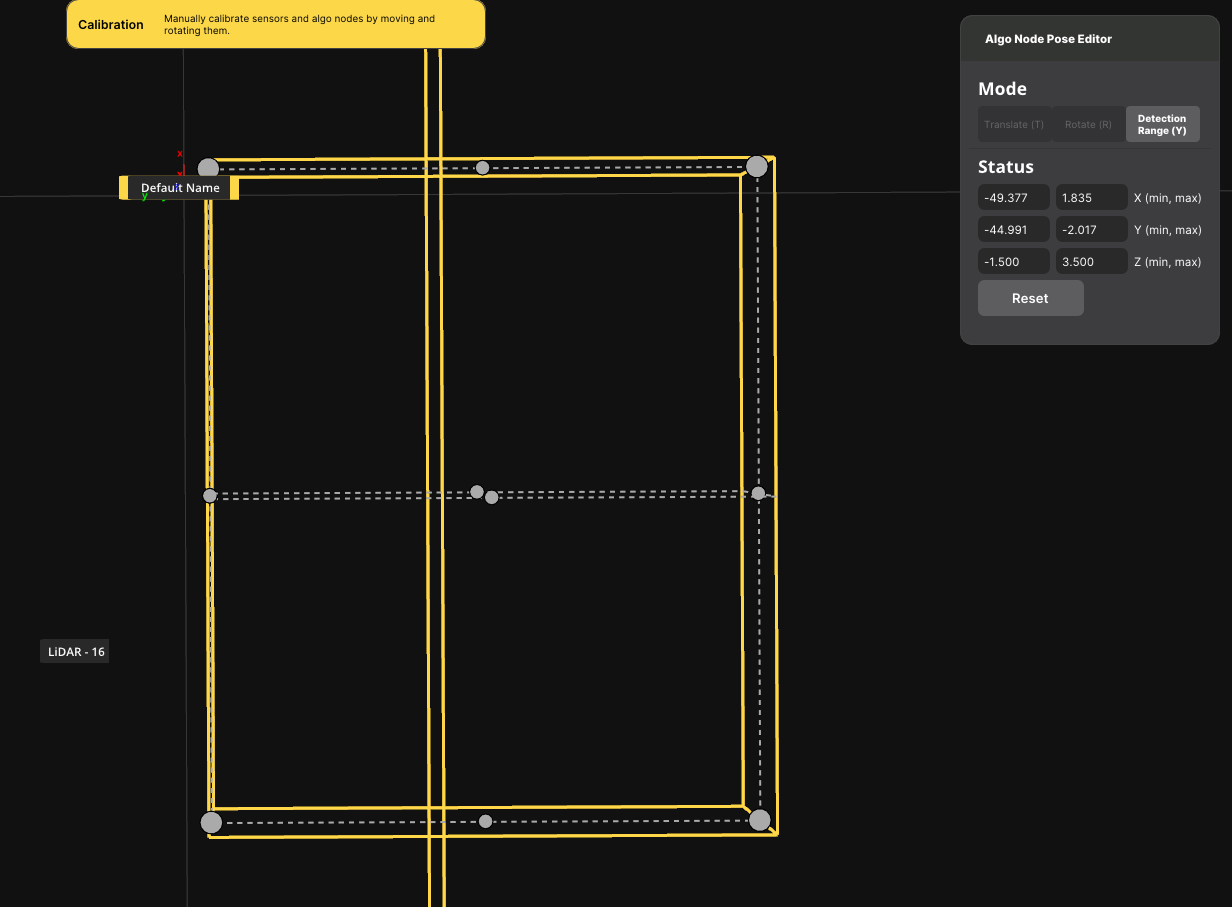
Important: Ensure there is a slight overlap between the new Algo Node and any adjacent Algo Nodes. This overlap allows the system to seamlessly track and merge objects as they move from one zone to another.
Step 4: Set the Local Parameters
Finally, apply your custom tuning.
- Navigate to the settings panel:
Settings > Algo Node Parameters > <Your New Algo Node Name>. - Adjust the parameters as needed for this specific zone.
- Click Save to apply the new settings.
Once saved, you can switch to Runtime Mode to see your local parameters take effect.